Ghana Salary Range: GHS 3,500 – GHS 5,000 per month (approximately USD 225 – USD 332) Factors:...
Blog
Teacher’s Salary in 10 Countries “Welcome back to the channel! Today, we’re diving into how much teachers...
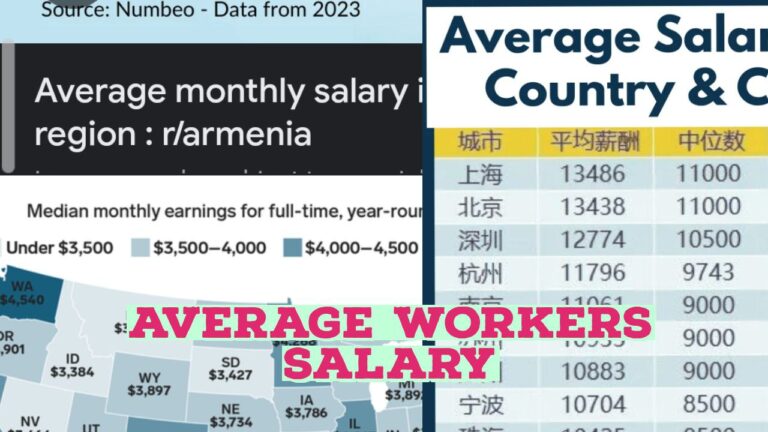
Average Salary of workers in top 10 countries Here’s an average salary comparison for various countries across...
Top Allowances Given to Workers Workers often receive various allowances from companies or governments to supplement their...
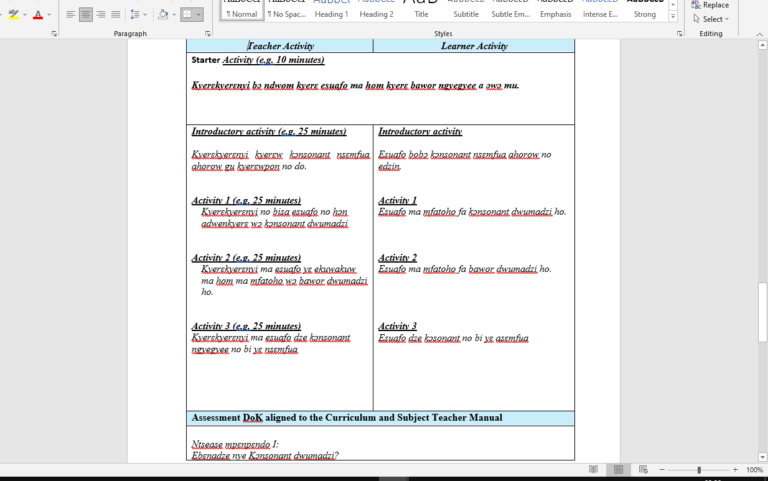
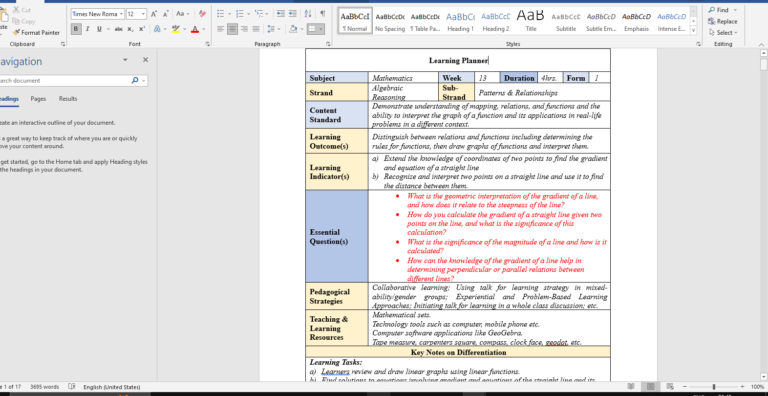
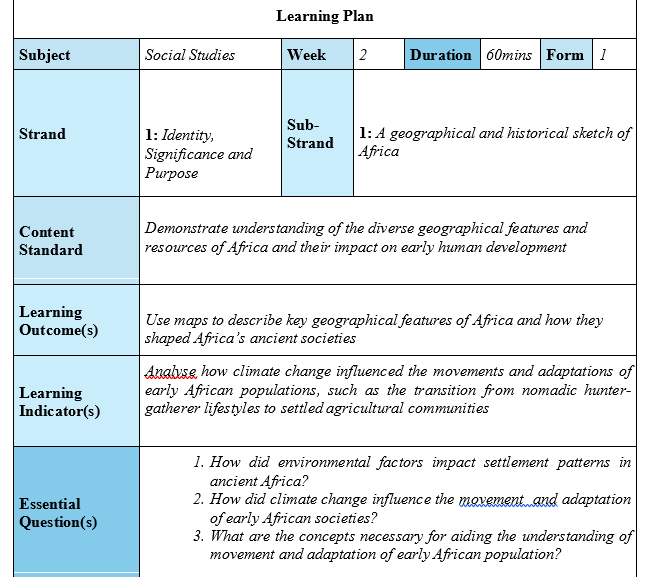
This is a sample of a Populated Learning Planner, you can use this to prepare yours Download...
Affordability Wahala: Your Loan Could be Cancelled if This Happens Before taking any loan or making deductions...
This is a sample of a Populated Learning Planner, you can use this to prepare yours Download...
Canada will sharply lower the number of immigrants it allows into the country for the first time...
Common Errors to Avoid in Transcript Applications to Universities, WES, Spantran, QECO, or for Personal Use ...
This is a sample of a Populated Learning Planner, you can use this to prepare yours Download...