How to use GESI responsive language and interaction as a Teacher The Teacher; 1) does not say...
GESI Lesson Plans
How to Use GESI responsive pedagogy in the classroom as a Teacher. The Teacher; 1) is conscious...
Terminologies to Know from the New SHS/SHTS/STEM Curriculum Familiarize yourself with some terminologies associated with the New...
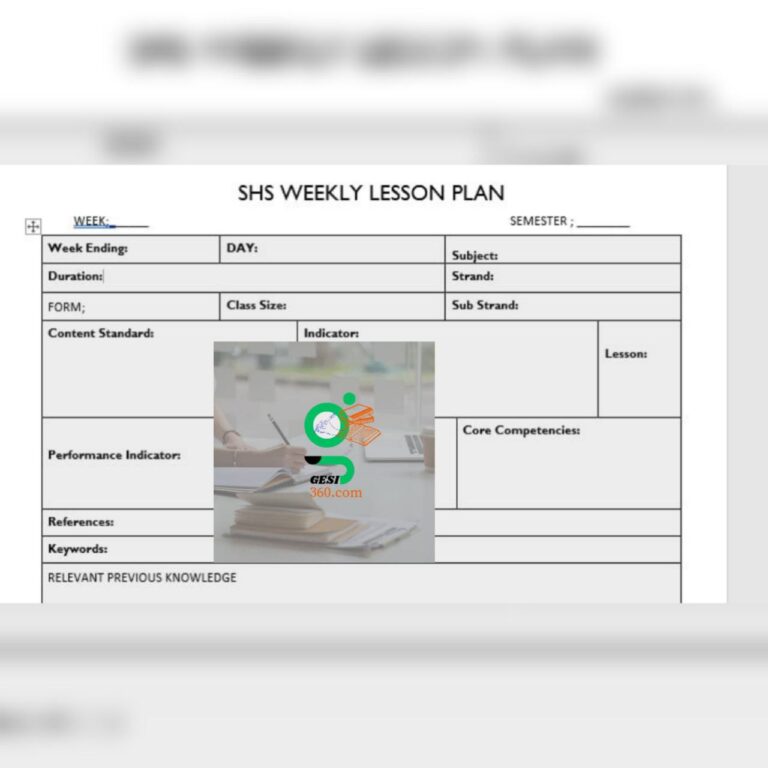
SHS New Weekly Lesson Plan Template For the New Curriculum ( GESI,SEL, ICT, 21st Century) There are...
GESI360.com is a blog for teacher professional development. There are many ways teachers teach around the globe,...